Power quality enhancement techniques refer to the methods used to improve the quality of electrical power, with the goal of reducing power interruptions, voltage sags, and other power disturbances that can harm electrical equipment and impact the reliability of the electrical grid. Here are some of the commonly used power quality enhancement techniques:
- Power Factor Correction (PFC): Power factor correction is the process of adjusting the phase angle between the current and voltage waveform to reduce the reactive power component and increase the power factor. This helps to reduce energy losses and improve the efficiency of the electrical system.
- Harmonic Mitigation: Harmonics are high-frequency distortions in the current waveform that can cause problems such as overheating, loss of efficiency, and interference with other equipment. Harmonic mitigation techniques include filters, passive damping, and active harmonic compensation systems to reduce the impact of harmonics on the electrical system.
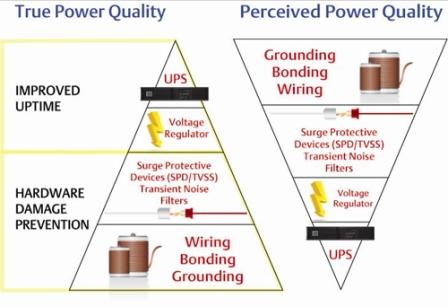
- Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS): A UPS provides backup power to equipment in the event of a power outage, ensuring that critical systems remain operational. UPS systems can provide a clean and reliable power source, reducing the risk of damage to equipment and minimizing downtime.
- Voltage Regulation: Voltage regulation is the process of maintaining the voltage level within a specified range, reducing the impact of voltage sags and surges on equipment. This can be achieved through the use of transformers, voltage regulators, and voltage stabilizers.
- Surge Protection: Surge protection devices protect electrical equipment from damage due to high voltage transients caused by lightning strikes, power outages, or other events. Surge protection devices can limit the voltage applied to the equipment and prevent permanent damage.
- Dynamic Voltage Restorer (DVR): A DVR is a type of power electronics device that can correct voltage sags and surges in real-time, providing a clean and stable voltage source to the electrical system.
By implementing these power quality enhancement techniques, the reliability and performance of the electrical system can be improved, reducing the risk of power disturbances and the negative impact on equipment and processes.
Here are some things to avoid in order to maintain power quality:
- Overloading electrical circuits: Overloading electrical circuits can lead to voltage sags, power interruptions, and increased energy losses. It’s important to monitor the load on electrical circuits and avoid overloading them.
- Poor wiring practices: Poor wiring practices such as improper grounding, undersized conductors, and loose connections can cause power disturbances and increase the risk of electrical failures.
- Ignoring power quality issues: Power quality issues should be addressed promptly, as they can cause harm to electrical equipment and disrupt the operation of processes. Ignoring power quality issues can lead to increased maintenance costs, decreased equipment lifespan, and unplanned downtime.
- Using outdated or inadequate equipment: Using outdated or inadequate equipment, such as old transformers, voltage regulators, and surge protection devices, can increase the risk of power disturbances and reduce the reliability of the electrical system.
- Not performing regular maintenance: Regular maintenance of electrical equipment and systems is essential for maintaining power quality. Neglecting maintenance can result in equipment degradation, decreased efficiency, and increased risk of power disturbances.
- Improper use of electrical equipment: Improper use of electrical equipment, such as connecting non-compatible equipment, can lead to power quality issues, as well as increase the risk of electrical fires and other safety hazards.
By avoiding these practices, the quality of electrical power can be maintained, reducing the risk of power disturbances and increasing the reliability and performance of the electrical system.